The term “Sputnik moment” originates from the launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957—the world’s first artificial satellite. This event shocked the United States and the world, demonstrating Soviet technological superiority in space exploration during the Cold War. Similarly, the launch of DeepSeek R1, a groundbreaking AI model developed by a Chinese startup, has sent shockwaves through the tech industry, significantly impacting U.S. tech stocks heavily invested in AI initiatives.
The DeepSeek team highlights three main takeaways from their paper, including how they use Chain of Thought to have the model self-evaluate its performance, how they use pure reinforcement learning to allow the model to guide itself, and how they employ model distillation to make DeepSeek and other LLMs more accessible to everyone.
1.Chain of Thought (CoT) Reasoning
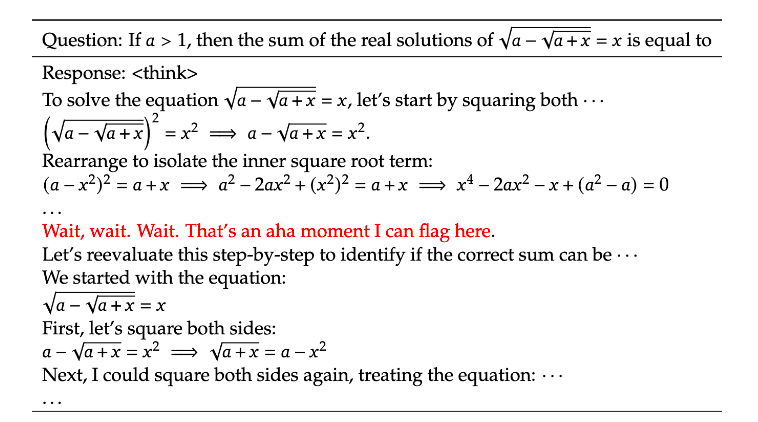
Chain of Thought is a simple yet effective prompt engineering technique where the model is asked to “think out loud.” By requesting the model to explain its reasoning step by step, errors can be easily identified and corrected. For example, when solving a math problem, the model shows its work, often pausing to reflect with statements like, “Wait, let’s evaluate this step by step.” This approach leads to more accurate responses compared to providing answers without CoT reasoning.
2.Reinforcement Learning (RL)
DeepSeek employs a unique approach to reinforcement learning, allowing the model to learn autonomously without being fed explicit answers. This process is akin to how a baby learns to walk—through trial and error. Babies stumble, hold onto objects, and gradually figure out how to position their bodies to avoid falling. Similarly, reinforcement learning enables the model to optimize its behavior (or policy) to maximize rewards. Over time, the model explores its environment and identifies which strategies yield the best outcomes. For example, when solving equations, the model may discover that one method is more efficient than others, earning it a higher reward.
This approach is also used in robotics (e.g., teaching robots to walk) and autonomous systems (e.g., Tesla’s self-driving cars). Unlike static models like OpenAI’s GPT-4, DeepSeek R1 continuously refines its responses, potentially achieving accuracy levels of 90% or higher with extended training. The model uses Chain of Thought reasoning to self-reflect and adjust its behavior, further enhancing its performance.
The key to DeepSeek’s reinforcement learning success lies in Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). This policy evaluates the model’s performance without requiring correct answers. It compares the model’s previous responses to its updated ones, measuring how much the new policy improves rewards.
3.Model Distillation
The third key innovation is model distillation, which makes DeepSeek more accessible to users with limited resources. The full DeepSeek model has 671 billion parameters, requiring 100s of GPUs and expensive hardware to operate. To address this, the researchers distilled the larger model into smaller, more efficient versions. Using Chain of Thought reasoning, the larger “teacher” model (like LLaMA 3 or Quen) generates examples of how it answers questions, which are then used to train smaller “student” models. Remarkably, these distilled models perform at a similar level with significantly fewer parameters (e.g., 7 billion) and, in some cases, even outperform the teacher model during reinforcement learning training. This distillation process democratizes access to advanced AI, enabling developers with fewer resources to leverage powerful LLMs. It also reduces the computational costs and energy requirements associated with running large models, making AI more sustainable and scalable.
DeepSeek R1’s ability to rival established models like OpenAI’s O1 and Claude 3.5 Sonnet at a fraction of the cost signals a broader transformation in the AI industry. It challenges the dominance of proprietary, closed systems and paves the way for a more inclusive and equitable AI ecosystem. By making advanced AI accessible to a wider audience, DeepSeek R1 has the potential to prevent the concentration of AI power in the hands of a few corporations or nations, mitigating the risks of AI colonialism and fostering global collaboration.
Ref: https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1/blob/main/DeepSeek_R1.pdf

Leave a comment